cck hormone secreted by|what does cck mean : Tagatay CCK plays important physiological roles both as a neuropeptide in the central nervous system and as a peptide hormone in the gut. It is the . See more UFC.COM - United States. Brazil; China; France; Japan; Korea; Latin America; Russia; USA Espanol; Footer. UFC. The Sport; UFC Foundation; Careers; Store; UFC Fight Club
0 · what does cholecystokinin target
1 · what does cck mean
2 · secretin and cholecystokinin
3 · hormone that impacts digestion
4 · cholecystokinin supplements
5 · cholecystokinin foods
6 · cck secretion chart
7 · cck peptide
Susana Reche Rank: 8819 Videos: 0 Viewed: 170 Sonia Rank: 449 Videos: 1 Viewed: 2.9k Windy Girk Rank: 1001 Videos: 0 Viewed: 891
cck hormone secreted by*******Cholecystokinin (CCK or CCK-PZ; from Greek chole, "bile"; cysto, "sac"; kinin, "move"; hence, move the bile-sac (gallbladder)) is a peptide hormone of the gastrointestinal system responsible for stimulating the digestion of fat and protein. Cholecystokinin, formerly called pancreozymin, is synthesized . See moreEvidence that the small intestine controls the release of bile was uncovered as early as 1856, when French physiologist Claude Bernard showed . See more
cck hormone secreted by what does cck meanCCK plays important physiological roles both as a neuropeptide in the central nervous system and as a peptide hormone in the gut. It is the . See more
• Antianalgesia• Cholecystokinin antagonist• Proglumide See moreCholecystokinin is a member of the gastrin/cholecystokinin family of peptide hormones and is very similar in structure to gastrin, another gastrointestinal hormone. CCK and gastrin . See moreCCK has been shown to interact with the cholecystokinin A receptor located mainly on pancreatic acinar cells and cholecystokinin B . See more
• Media related to Cholecystokinin at Wikimedia Commons• Cholecystokinin at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) See more
Cholecystokinin is a hormone that functions as part of your digestive system. It’s released (secreted) by your small intestine during the digestive process. It's . Cholecystokinin is secreted by cells of the upper small intestine. Its secretion is stimulated by the introduction of hydrochloric acid, amino acids, or fatty acids into the .
Cholecystokinin is a gut hormone released after a meal, which helps digestion and reduces appetite. Alternative names for cholecystokinin. Cholecystokinin used to be known as . Cholecystokinin (CCK) is a peptide hormone linked to the gastrointestinal (GI) system. The receptors are expressed in the central nervous system[1] specifically in the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, . Cholecystokinin (CCK) is the major hormone responsible for gallbladder contraction and pancreatic enzyme secretion. CCK, like other gastrointestinal hormones, .
Cholecystokinin (CCK), formerly referred to as pancreozymins, is another hormone-like secretin used in the pancreas's stimulation. Secretin mainly stimulates the secretion of pancreatic .
The following story about cholecystokinin (CCK) illustrates how studies of a single peptide hormone from the gut (CCK-33) has gradually contributed to expand .Cholecystokinin (CCK), a hormone secreted by the intestine after ingestion of lipids and proteins, slows gastric emptying and triggers satiety in a wide variety of species [64].It is secreted from mucosal epithelial cells in the first segment of the small intestine (duodenum), and stimulates delivery into the small intestine of digestive enzymes from .
Due to this discovery and the implications of CCK’s therapeutic potential for eating disorders, considerable attention has focused on the study of this hormone. In the gastrointestinal tract, CCK is secreted by discrete enteroendocrine cells (EECs) which contain intermediate-size secretory granules (I cells) (95).
cck hormone secreted by Endocrine hormones are secreted from enteroendocrine cells directly into the bloodstream, passing from the portal circulation to the systemic circulation, before being delivered to target cells with .
Cholecystokinin, otherwise known as CCK or CCK-PZ, is a hormone that was once called pancreozymin because of its actions on the pancreas. This hormone has receptors through the central nervous system and gut, impacting several areas of the body. . Cholecystokinin is a hormone produced in the I-cells that line the duodenum. The . GI hormones secreted in response to eating, however, were mainly considered to be phasic signals sculpting the timing and size of individual meals and were not thought to be relevant for the tonic control of total energy intake and body-weight regulation (e.g., Refs. . CCK is secreted in response to the products of carbohydrate, . Cholecystokinin (CCK), formerly referred to as pancreozymins, is another hormone-like secretin used in the pancreas's stimulation. Secretin mainly stimulates the secretion of pancreatic juice, which contains pancreatic enzymes and acts on the gallbladder, which can assess gallbladder function.[1] CCK increases pancreatic enzyme . A number of gut hormones, including cholecystokinin (CCK), GLP1 and PYY, provide feedback control of gastric emptying 10. . Gut hormones are produced by enteroendocrine cells .
Cholecystokinin (CCK) is an important hormonal regulator of the digestive process. CCK cells are concentrated in the proximal small intestine, and hormone is secreted into the blood upon the ingestion of food. The physiological actions of CCK include stimulation of pancreatic secretion and gallbladder contraction, regulation of gastric emptying .GI hormones are a large family of peptides and are secreted by endocrine cells that are widely distributed throughout the GI mucosa and pancreas. Gastrin, secretin, and cholecystokinin (CCK) were the first discovered gut hormones, and as of today, there are more than 50 gut hormone genes and a multitude of bioactive peptides, which makes .Cholecystokinin (CCK) is secreted from endocrine cells that are concentrated in the proximal small intestine, but found throughout the length of the small intestine. The postprandial release of CCK is key in the activation of intestinal feedback control of gastrointestinal function, comprising short term inhibition of gastric emptying and acid . Identification Generic Name Cholecystokinin DrugBank Accession Number DB08862 Background. Cholecystokinin ( also known as CCK or CCK-PZ) is a peptide hormone of the gastrointestinal system which is responsible for stimulating the digestion of fat and protein.Cholecystokinin, previously called pancreozymin, is synthesized and .
Cholecystokinin also known as CCK or CCK-PZ, is a peptide hormone of about 33 amino acids, secreted by the enteroendocrine cells in the duodenum (the first portion of the small intestine) and also found in the central nervous system, specifically in the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and striatum 1. Cholecystokinin receptors are . CCK is produced along the entire small intestine, with the highest density of CCK hormone-expressing cells in the duodenum [19,20,37]. Several transcriptomic [ 16 , 17 , 37 ] and immunohistochemical [ 37 , 38 ] studies demonstrated co-expression of CCK with other gut hormones including GIP, GLP-1, secretin and neurotensin.
what does cck meanThe prehistory. Almost a century before CCK was discovered in 1928 as a gallbladder-emptying hormone (), European physiologists took a broad interest in bile secretion and the role of bile in digestion (for reviews, see 12, 13).For instance, Claude Bernard (who introduced the concept of ‘sécrétion interne’) reported in 1856 that installation of .The hormone CCK is produced by L-cells in the small intestine and its secretion in the duodenum induces the release of enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the gallbladder. Studies from the Herness group ( Herness et al, 2002 ; Shen et al, 2005 ) presented novel data demonstrating that CCK is expressed in a subset of TRCs, and that it may .
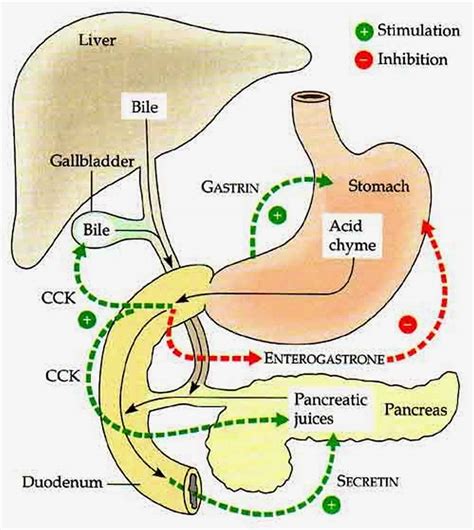
Cholecystokinin also known as CCK or CCK-PZ, is a peptide hormone of about 33 amino acids, secreted by the enteroendocrine cells in the duodenum (the first portion of the small . CCK is produced along the entire small intestine, with the highest density of CCK hormone-expressing cells in the duodenum [19,20,37]. Several transcriptomic [ 16 , 17 , 37 ] and immunohistochemical [ 37 , 38 ] studies demonstrated co-expression of CCK with other gut hormones including GIP, GLP-1, secretin and neurotensin.The prehistory. Almost a century before CCK was discovered in 1928 as a gallbladder-emptying hormone (), European physiologists took a broad interest in bile secretion and the role of bile in digestion (for reviews, .The hormone CCK is produced by L-cells in the small intestine and its secretion in the duodenum induces the release of enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the gallbladder. Studies from the Herness group ( Herness et al, 2002 ; Shen et al, 2005 ) presented novel data demonstrating that CCK is expressed in a subset of TRCs, and that it may .
Cholecystokinin (CCK) is a major gastrointestinal hormone that plays an important role in stimulation of pancreatic secretion and gall-bladder contraction, regulation of gastrointestinal motility and induction of satiety. . Thus, the CCK-RF are spontaneously secreted into the intestinal lumen in humans, while the CCK-producing cells are under .Abstract. Gastrin and CCK (cholecystokinin), gut hormones first secreted after postprandial stages, share the C-terminal amino acids and some types of receptors to be stimulated. Both types of hormone-secreting cells are typical open-type cells which detect foods and their digested elements in the lumen and regulate the secretion of gastric . After the discovery in 1928 (), CCK became part of the classical troika of gut hormones together with secretin and gastrin.The last decades, however, have shown that CCK, in addition to its local acute functions in digestion (gallbladder emptying and pancreatic enzyme secretion), is also a growth factor, a neurotransmitter in the brain and . In collaboration with physiologist W. M. Bayliss, English physician E. H. Starling discovered secretin in 1902.[1] During that era, hormonal control of pancreatic secretions conflicted with the teachings of the Pavlov school that only neural reflexes were involved in pancreas response to duodenal acidification.[2] The findings of Bayliss and .CCK is the first of a repertoire of hormones that regulate gastric emptying. The next section details the effects of several gastrointestinal and other hormones on gastric emptying. . Amylin is a peptide hormone co-secreted with insulin by the β-cell. Consequently, amylin is deficient in type 1 diabetes, while plasma levels are increased in .

Secretin is a polypeptide hormone secreted by the enteroendocrine S cells located within the crypts of Lieberkuhn in the duodenum and proximal jejunum in response to the presence of . Somatostatin inhibits the secretion of multiple hormones (GH, TSH, ACTH, gastrin, CCK, secretin, insulin and glucagon) and gastric, intestinal and .
The salivary glands secrete more saliva in response to stimulation by the autonomic nervous system triggered by food in preparation for digestion. Simultaneously, the stomach begins to produce hydrochloric acid to digest the food. . Secretin acts in tandem with another hormone called cholecystokinin (CCK). Not only does CCK stimulate the .
Similarly, the gut hormones produced and secreted by the enteroendocrine cells (EECs) also have a wide range of targets and undoubtedly play pleiotropic and important roles in maintaining health. . CCK is a gut-derived peptide hormone that is produced and released by the enteroendocrine I cells located in the mucosal epithelium .
Resultado da 29 de jul. de 2021 · Conheça o Painel de Senhas sustentável do WorkLab . Sem impressão de papel, muito moderno e fácil de utilizar.
cck hormone secreted by|what does cck mean